计算理论:迁移系统
Transition System
Definition
Transition System
TS 是一种 reactive system
It is used to describe the potential behavior of discrete systems. It consists of states and transitions between states, which may be labeled with labels chosen from a set; the same label may appear on more than one transition.
如果用图像来表示,TS 是一个二元图,node 代表 state,edge 代表 transition
更为正式的定义为
一个 TS 是一个 5-tuple
是 state set(可以是无限甚至不可数的) 是初始的状态 是 transition set(可以是无限甚至不可数的) 是两个从 到 的映射,对于 , 代表其 source 和 target
如果
Reachable and Terminal
如果一个 transition
根据此给出更为 general 的 transition
Basis. 如果
Induction. 如果
根据此即可定义一个状态的可达(reachable)
对于 TS
而如果对于
若
Path
一条长度为
上述定义是 finite path,而一个 infinite path 是一个 infinite 的 transition 序列
若将所有 finite path 的集合记为
同样的,
由此可以定义
为长度为
product 也可推广到
Empty path:对于每个状态
则如果对于 path
Labeled transition system
A transition system labeled by an alphabet
其中
label
一般来说不会有两个 transition 有相同的 source,target 以及 label,即 TS 中的 transition 都是可区分的(
在 labeled TS 中,有 path
Equivalency for TS
等价关系是一种二元关系,满足自反,对称,传递。对于 TS 有很多种不同的等价定义方式
Homomorphism: 考虑两个 TS
从
满足
对于 labeled TS 还需满足
如果
strong isomorphism: 一个 TS strong isomorphism 是一个 TS homomorphism,满足
显然如果
对于两个 strong isomorphic 的 TS,它们唯一的区别就是命名方式
weak isomorphism: 对于一个 TS
则如果两个 TS 的 isomorphism 是定义在
显然,如果两个 TS isomorphic,则这两个 TS weak isomorphic
Bisimulation: 令
Basis.
Induction.
- 如果
且 ,则存在 满足 并且 - 如果
且 ,则存在 满足 并且
这里的 transition 需要 label 相同(或是对应)
两个 isomorphic 的 TS 一定是 bisimilar 的,但反之不真
Free Product of TS
考虑
则其 free product
对于 labeled TS 同理
然而对于 product TS 来说,不是所有 transition 都是有意义的,因为要受到同步的限制
故有意义的 TS 是 free product 的一个子系统,其定义可表示为 synchronous product
如果 TS
是 free product 的子系统,仅包含满足
在 free product 中,假设所有的 TS 都是同步执行的,但是有时候也需要体现出某个 TS 执行而其他 TS 没有执行的情况,故可以引入
在不同 TS 间有 shared label 的情况下
Temporal Logic
Temporal Logic 用于形式化描述 reactive system 中 transition 的序列,而其中的属性可以用 CTL* 来描述
CTL* 可以用来描述 computation tree 的属性,computation tree 是从 TS 开始状态的所有可能执行路径
CTL* 的组成包括
- path quantifier: A (for all computation path), E (for some computation path)
- temporal: X, F, G, U, R
- X (next time): the property holds in the second state of the path
- F (eventually): the property will hold at some state on the path
- G (always): the property holds at every state on the path
- U (until): if there is a state on the path where the second property holds, at every preceding state, the first one holds
- R (release): the second property holds along the path up to and include the first state where the first property holds. However, the first property is not required to hold eventually
一个例子如下
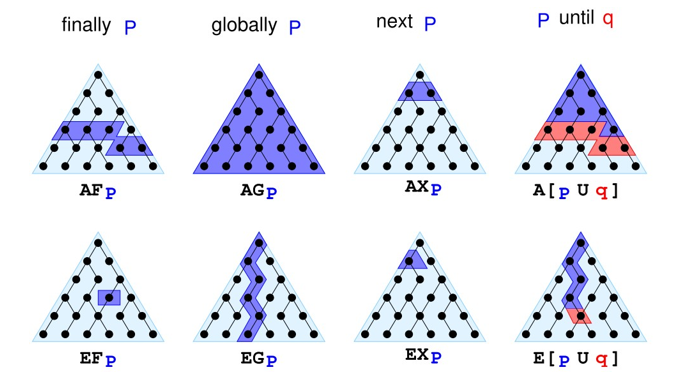
常见的用 CFL 描述的行为有
- Safety: something bad will not happen,常用 AG 描述
- Liveness: something good will happen,常用 AF 描述
- Fairness: something is successful/allocated infinitely often,常用 AGAF 描述,即对于所有路径上的所有状态,都满足在之后的所有路径上都会在某个状态上满足条件